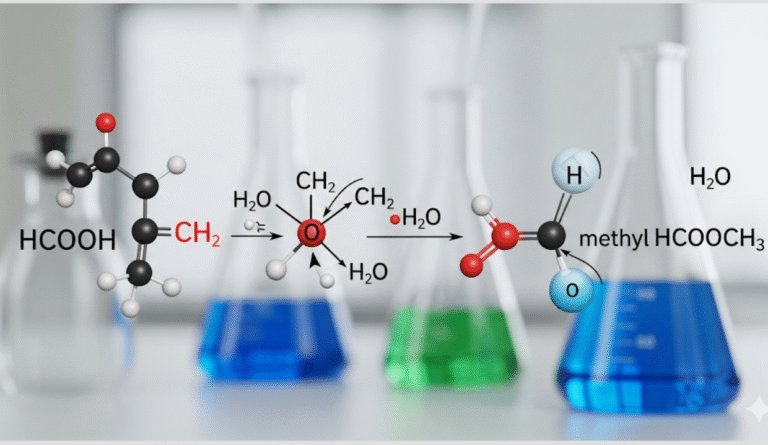
When you see the formula HCOOH CH₂ H₂O, it often causes confusion. In reality, the chemistry points to methyl formate (HCOOCH₃), an ester closely related to formic acid (HCOOH). This compound has fascinating behavior, especially in its reaction with water (H₂O) through a process called hydrolysis.
Understanding this connection is important because methyl formate plays a role in green chemistry, fuel cell technology, and industrial uses like leather tanning and solvent production. In this guide, we’ll explore its structure, properties, reactions, and applications, making the topic clear for both students and professionals.
Understanding the Formula
| Compound | Formula | Role in Reaction |
|---|---|---|
| Formic Acid | HCOOH | Reactant |
| Methylene | CH2 | Reactant |
| Water | H2O | Reactant |
| Methyl Formate | HCOOCH3 | Product |
The formula HCOOH CH₂ H₂O can look tricky at first. HCOOH is formic acid, the simplest carboxylic acid, while CH₂ points to its link with formaldehyde. When combined, they represent methyl formate (HCOOCH₃), an ester created from formic acid and methanol.
Adding water (H₂O) highlights how this ester reacts through hydrolysis, breaking down into formic acid and methanol again. Understanding this formula helps explain both its structure and its chemical behavior.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Methyl Formate
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 60.05 g/mol |
| State | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Pleasant, ether-like |
| Boiling Point | 31.5 °C |
| Density | 0.97 g/cm³ |
Methyl formate (HCOOCH₃) is a colorless liquid with a sweet, fruity smell, common in the ester family. It is highly flammable, has a boiling point of about 32 °C, and mixes easily with water (H₂O) and alcohols.
The compound is lighter than water and evaporates quickly, making it useful as a solvent. Chemically, it is reactive in hydrolysis and esterification processes, where it can produce formic acid (HCOOH) and methanol under specific conditions.
Reaction of Methyl Formate with Water
When methyl formate (HCOOCH₃) reacts with water (H₂O), it undergoes hydrolysis, breaking down into formic acid (HCOOH) and methanol. This reaction can happen slowly on its own but is much faster in the presence of acid or base catalysts.
In laboratories, it demonstrates how esters convert back to acids and alcohols. This simple process is important in both industrial chemistry and green fuel research, where formic acid is valued as a hydrogen source.
Industrial Production of Methyl Formate
Industrially, methyl formate is made by reacting methanol with carbon monoxide in the presence of a sodium methoxide catalyst. This process is widely used because it is cost-effective and efficient. The reaction takes place under controlled temperature and pressure conditions to ensure high yield.
Methyl formate is also produced as a by-product in some chemical industries. Its large-scale production makes it valuable for creating formamides, formic acid, and fuel additives in the global chemical market.
Also read: NTDTVJP: Japan’s Independent Media Shaping Global Influence
Uses of Methyl Formate
Methyl formate has many important uses in daily life and industries. It acts as a solvent for resins, oils, and cellulose. It is also used as a blowing agent in foam production and as a fumigant for pest control.
In chemical industries, it serves as a building block to make formamides, formic acid, and dimethylformamide (DMF). Its role in fuel additives also helps improve energy efficiency. These diverse applications make methyl formate a highly valuable chemical compound.
Safety and Environmental Impact of Methyl Formate
| Risk Factor | Effect | Safety Measure |
|---|---|---|
| Flammability | Highly flammable | Keep away from flames |
| Health Hazard | Irritates skin and eyes | Wear protective gear |
| Inhalation | Affects lungs | Use proper ventilation |
| Environment | Breaks down in air | Avoid spills in soil/water |
Methyl formate should be handled with care because it is flammable and can irritate the skin, eyes, and lungs. In workplaces, proper ventilation and protective gear are important for safety.
Environmentally, it breaks down quickly in the air and does not build up, which lowers long-term risks. However, spills or careless use can still harm water and soil. Overall, safe handling practices are essential to reduce both health hazards and environmental impact.
Reaction Mechanism in Organic Chemistry
In organic chemistry, the reaction of HCOOH with CH2 and H2O shows how simple molecules can transform into useful compounds like methyl formate. The mechanism usually involves nucleophilic attack followed by bond rearrangements, creating a stable ester.
Understanding this step-by-step process helps students and researchers see how bonds break and form. It also explains why certain conditions, such as heat or catalysts, are needed for efficiency. This reaction is a good example of basic organic transformations.
Industrial and Laboratory Applications
| Application | Industry/Use |
|---|---|
| Solvent | Coatings, adhesives |
| Blowing Agent | Polyurethane foams |
| Intermediate | Chemical manufacturing |
| Research | Organic synthesis studies |
Methyl formate has many practical uses in both industry and laboratories. In industry, it works as a solvent, blowing agent for foams, and an intermediate for making other chemicals. Laboratories often use it in organic synthesis to study esterification and related reactions.
Its quick evaporation and moderate toxicity make it useful but require careful handling. Because of its versatility, methyl formate remains an important compound in chemical research and manufacturing across different sectors.
FAQS HCOOH CH2 H2O
What is the reaction between HCOOH, CH2, and H2O?
This reaction produces methyl formate, an ester formed when formic acid reacts with methylene and water under suitable conditions.
What is the use of methyl formate in industry?
Methyl formate is used as a solvent, in making foams, and as an intermediate for producing other important chemicals.
Is methyl formate safe to handle?
Methyl formate is flammable and can irritate skin, eyes, and lungs. It must be handled with protective gear and proper ventilation.
Why is this reaction important in organic chemistry?
It’s a good example of esterification and teaches how simple molecules combine to form esters, which are widely used in chemistry and industry.
Does methyl formate harm the environment?
Methyl formate breaks down quickly in air, so it doesn’t persist. However, spills in soil or water can cause short-term environmental harm.
Conclusion
The reaction of HCOOH with CH2 and H2O shows how simple chemicals can produce valuable compounds like methyl formate. This ester has wide applications in industry, research, and everyday products.
By understanding its formation, properties, and safety concerns, students and professionals can appreciate both the science and practical value behind it. With proper handling, methyl formate serves as a safe and versatile chemical, making it an important topic in organic chemistry and chemical engineering.